excited state electron configuration|What electron configuration represents : Pilipinas You should be able to identify both ground and excited state electron configurations. Example 1 : What is the ground state electron configuration of carbon ? Answer : Carbon is the 6th element in the periodic table, hence the . Al-Anabi Racing consisted of Top Fuel driver Del Worsham and the driver Schumacher considers his biggest rival, Larry Dixon. Many fans and media members felt Schumacher would not have the success he had in previous years as Johnson was the Army Top Fuel team's tuner during his run of five consecutive titles. Schumacher met Dixon and .
PH0 · What electron configuration represents an excited state?
PH1 · What electron configuration represents an atom in the
PH2 · What electron configuration represents
PH3 · Introduction to Excited Electronic States
PH4 · Excited state
PH5 · Excited States
PH6 · Excited Electronic States
PH7 · Electron configuration
PH8 · Ch 1 : Orbital Fillling & Electron configurations
PH9 · Ch 1 : Orbital Fillling & Electron configurations
PH10 · Ch 1 : Orbital Fillling & Electron configur
PH11 · 8.3: Electron Configurations
PH12 · 20.3: Excited Electronic States: Electronic
PH13 · 10.10: Electronic States
Taya777's Betting Exchange lets you bet against other people and get great odds on thousands of markets every day. Best Odds Bet In-Play Cash Out.
excited state electron configuration*******Learn how to identify an excited state electron configuration by looking at the valence electron's orbital. See examples of oxygen in ground and excited states, and the difference between 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 and 1s^2 2s^2 2p^3 3s^1.excited state electron configuration What electron configuration represents Learn how molecules absorb light of different wavelengths when electrons jump from lower to higher energy orbitals. Explore examples of σ-σ*, π-π*, and n-π* .
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of p.You should be able to identify both ground and excited state electron configurations. Example 1 : What is the ground state electron configuration of carbon ? Answer : Carbon is the 6th element in the periodic table, hence the .
Learn how to describe the distribution of electrons in atoms or molecules using atomic or molecular orbitals. Find out the notation, rules, and examples of electron configurations for .How do we build from there to construct an excited-state wave function? Correlated Methods. I. Configuration Interaction. A Hartree-Fock one-electron orbital (wave function) is expressed . Learn about the electronic configuration and states of atoms and molecules, and how they are affected by spin, orbital, and symmetry properties. Find out how to label and .
Learn about the types, properties and modeling of excited electronic states in chemistry. This web page covers the basics of electronic transitions, valence and Rydberg states, multi . By “building up” from hydrogen, this table can be used to determine the electron configuration for any atom on the periodic table. We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram .
L=0: ground state, L>0: excited states. For non-interacting electrons, excited states are just excited determinants and the excitation energies are orbital energy differences An excited state means that (typically) the valence electron has moved from its ground state orbital (i.e. lowest available energy) to some other higher energy orbital. So any electron configuration in which the last electron (again, the valence electron) is in a higher energy orbital, this element is said to be in an excited state. For example, if we look at the .
Therefore, the electron configuration of sulfur(S**) in an excited state will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 3p x 1 3p y 1 3p z 1 3d xy 1 3d yz 1. This electron configuration shows that the last shell of the sulfur atom has six unpaired .You should be able to identify both ground and excited state electron configurations. Example 1 : What is the ground state electron configuration of carbon ? Answer : Carbon is the 6th element in the periodic table, hence the .Excited Electronic State Ultraviolet / visible (UV/vis) spectra are dominated by electronic transitions Electronic transitions typically occur in the 1-12 eV range . Configuration Interaction Singles (CIS) Simplest ab initiotreatment of excited states Has necessary determinants to . An electron configuration representing an atom in the excited state will show a valence electron promoted to a higher energy level. Example The ground state electron configuration of sodium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^1. In its excited state, the valence electron in the "3s" sublevel is promoted to the "3p" sublevel, giving the electron . For instance, the ground state electronic configuration of calcium (Z=20) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2. The calcium ion (Ca 2+), however, has two electrons less. Hence, the electron configuration for Ca 2+ is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6. Since we need to take away two electrons, we first remove electrons from the outermost shell (n=4). In this .Figure 6.29 shows the lowest energy, or ground-state, electron configuration for these elements as well as that for atoms of each of the known elements. Figure 6.29 This version of the periodic table shows the outer-shell electron configuration of each element. Note that down each group, the configuration is often similar. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially. Electron configuration of fluorine in the excited state. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital in the excited state. This is called a quantum jump. The ground-state electron configuration of fluorine is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. We already know that the p-subshell has three .
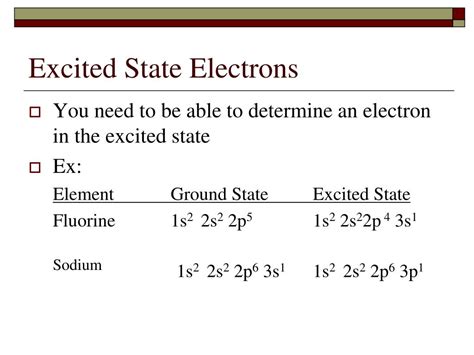
Excited states have the same number of electrons as the ground state atom, whereas an ionic configuration will have a different a number of electrons than the atom it came from. Wize Tip For excited states, the Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule can be disobeyed, but the Pauli Exclusion Principle must ALWAYS be followed. The p-subshell can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the remaining four electrons enter the 2p subshell. Therefore, the complete electron configuration of oxygen will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4. Note: The unabbreviated electron configuration of oxygen is [He] 2s 2 2p 4. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially. Electron configuration of manganese in the excited state. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital in an excited state. This is called .
What electron configuration represents Therefore, the electron configuration of nickel(Ni*) in an excited state will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d xy 2 3d yz 2 3d zx 2 3d x 2-y 2 1 3d z 2 1 4s 1 4p x 1. The valency of the element is determined by electron . Shorthand Electron Configuration Full Electron Configuration Electron shell arrangement; 1: Electron configuration of Hydrogen (H) 1s 1: 1s 1: 1: 2: Electron configuration of Helium (He) 1s 2: 1s 2: 2: 3: Electron . Therefore, the complete electron configuration of beryllium will be 1s 2 2s 2. Note: The unabbreviated electron configuration of beryllium is [He] 2s 2. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially. Electron configuration of beryllium in the excited state. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another in an excited state. 3. Continue the electron configuration from the noble gas until you reach the element of interest. 4. Put the noble gas in brackets and write the remainder of the electron configuration. Na has the same electron configuration as Ne with the addition of 3s 1. Na's noble gas configuration is [Ne]3s 1.

Example \(\PageIndex{1}\) : Electron Configuration; Example \(\PageIndex{2}\) : Bond Order; In order to explain both the ground state and the excited state involved in an absorption band in the ultraviolet and visible spectra of molecules, it is necessary to look at the electronic structure of molecules in somewhat different terms from the description given in the . Quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers n, l, m l, and m s.The principal quantum number n is a positive integer (1,2,3,4) and it represents the energy of the orbital.The angular momentum quantum number l, is from 0 to n – 1. The l values of 0, 1, 2, and 3 correspond to the s, p, d and f orbitals, respectively. The magnetic quantum number m l .
When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially. Vanadium excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital in the excited state. This is called quantum jump. The ground state electron configuration of vanadium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 3 4s 2.
Descriptive statistics refers to the process of summarizing numerical and categorical data in a concise and informative manner. It involves using various measures, such as measures of center, variability, shape, and location, to describe key features of the data. Descriptive statistics form the foundation for quantitative analysis and provide .
excited state electron configuration|What electron configuration represents